Comments from Expert Advisory Committee
- Acute exacerbations may be triggered by a viral or bacterial infection.
- Initiate short-acting bronchodilator therapy and 5 day course oral prednisolone 40 mg per day (30 mg per day if 60kg or less).
- Ensure all patients are up to date with influenza vaccine, COVID-19 vaccine and pneumococcal vaccine.
- Use first line antibiotics at recommended doses if sputum colour changes and increases in volume or thickness.
- Consider sending sputum for culture if frequent exacerbations or infections are slow to resolve. Sputum culture and sensitivity will help guide choice in treatment failure.
- In penicillin allergy, doxycycline is the preferred choice. Macrolide warning.
- The quinolones e.g. levofloxacin, ciprofloxacin are generally not appropriate as first line treatment in the community as there are safer alternatives available. Fluoroquinolone Warning.
- If considering a quinolone in a patient colonised with Pseudomonas spp, ciprofloxacin is the quinolone of choice. Consult microbiologist / infectious diseases physician for treatment choice and dose.
- Azithromycin should not be used for prophylaxis / prevention of exacerbations of COPD except under the direction of a respiratory physician. It is effective in a very select subgroup of COPD patients.
Treatment
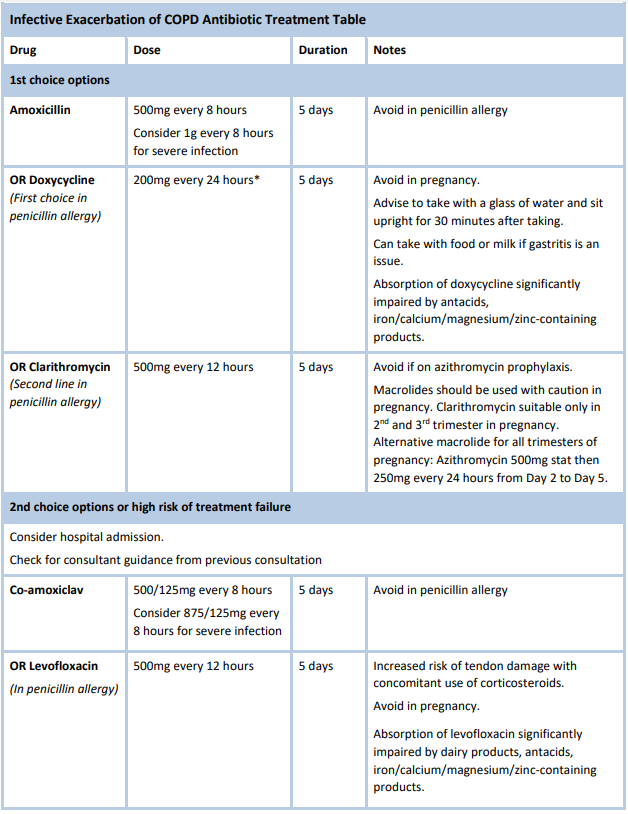
* Alternative doxycycline dose: 100mg every 12 hours.
In non-severe infection, 200mg stat then 100mg every 24 hours can be considered.
Patient Information
Useful Link
Reviewed October 2021
