What is an Improvement Collaborative?
An Improvement Collaborative is a systematic approach to quality improvement in which organisations test and measure practice innovations and then share their experiences to accelerate learning and widespread implementation of best practice. Improvement Collaboratives have been used internationally for over 20 years as a successful strategy for employing QI methods and approaches.
The Collaborative Handbook
- The Improvement Collaborative Handbook was designed to support staff and teams who wish to implement an Improvement Collaborative in their service. This Handbook provides background information and a step-by-step approach to organising and leading short-term Improvement Collaboratives, bringing together teams from various healthcare settings to address focused topics.
- This Handbook shares learning from the National QPS Directorate, which has successfully delivered a range of national Collaboratives for over a decade on topics such as reducing pressure ulcers, reducing harm from falls, and improving medication safety. Using the HSE Framework for Improving Quality, the Directorate has tested and adapted the Institute for Healthcare Improvement’s Breakthrough Series Collaborative Model for an Irish context. This model has been further adapted and updated relative to the post-COVID world in which we live by maximising the use of audio-visual telecommunications to facilitate online meetings so that participating teams can minimise travel and participate in the Collaborative virtually.
Why Quality Improvement?
Quality Improvement (QI) is a well-established, evidenced based approach to understanding processes and systems, pinpointing improvement opportunities, and designing sustainable solutions. Using the Model for Improvement, QI approaches can help services overcome common barriers to quality care, even in the context of resource and staffing constraints.
How does a Collaborative Work?
Improvement Collaboratives use a structured approach to support individuals, teams, and systems all at the same time. The shared learning and mutual support that comes from participating in a Collaborative motivates professionals to do things differently, which in turn becomes an effective vehicle for change to improve patient outcomes, service use and costs. It involves:
- Team-based learning sessions
- Identifying and testing changes for improvement
- Continuous sharing of ideas, learning, and best practice
- Identification of an important quality or safety goal.
How long does a Collaborative take?
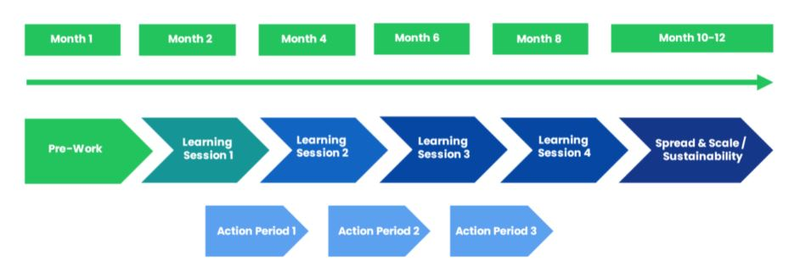
Collaboratives typically take 10-12 months to complete, following a series of learning sessions, action periods, measurement and evaluation, and summative reports. The figure below shows the sample phases and timeline for an Improvement Collaborative. Remember, these timelines are flexible and adaptable to your unique context. Your dedication and teamwork will steer the pace of your Collaborative's success.
Key Roles within the Collaborative
Collaborative Lead: The Collaborative Lead assumes overall responsibility for the Collaborative design, coordination, delivery and evaluation across the organisation, supported by a Collaborative Advisory Group.
Clinical Champion: Most often a front-line clinician responsible for guiding the design and delivery of the Collaborative from a clinical perspective.
Collaborative Advisory Group: Members provide specific clinical expertise and QI technical knowledge and skill sets to support the planning, development and delivery of the Collaborative.
Site Leads: Each participating service designates a Site Lead. The Site Lead may be a local Quality and Patient Safety leader or a senior clinician with experience in QI. The Site Lead is crucial in facilitating and guiding improvement efforts locally.
Project Teams: Every Site will have one or more Project Teams, each with a Team Lead and 3-8 Team Members. The Team Lead provides leadership and direction to the team, while the members actively contribute to the project's activities and work collaboratively towards achieving the improvement goals. Within a Collaborative, it is customary for 2-3 members of the Project Team to participate in all Collaborative activities, whilst the other Team members continue the work of the project at base and are guided by the learning of the team members participating in the Collaborative.
Holistic, sustained benefits include:
- QI methods enhance resource allocation and patient safety
- Eliminate inefficiencies, boost technology adoption and staff satisfaction
- Forge collaborations, improve patient handovers, and scale innovations
- Cultivate a positive workplace culture and develop vital professional skills
A key factor in successful Improvement Collaboratives is local ownership. A Collaborative should be coordinated and driven by people working within the service, engaging with staff to encourage them to creatively develop solutions for local challenges and to enable clear collective ownership of goals. The National QPS Directorate can offer coaching, mentoring, advice, and signposting to useful resources to support your Improvement Collaborative.
Contact Us
For more information on the Improvement Collaborative Handbook, contact the QPS Improvement Team at QPS.Improvement@hse.ie