Comments from Expert Advisory Committee
- Bacterial Vaginosis (BV) is a common cause of abnormal vaginal discharge in women of reproductive age. It is not considered to be sexually transmitted.
- It is characterised by a white, non-irritating, malodorous vaginal discharge. The discharge commonly smells "fishy" and this odour is often more noticeable after sexual intercourse
- The diagnosis can be made clinically on the basis of the description and appearance of the discharge. Typically the normal pH of the vagina is increased from normal (<4.5) to above 4.5 and up to 6.0 reflecting the replacement of normal lactobacilli with anaerobic organisms. Treatment can be started without doing a high vaginal swab (HVS). A diagnosis of BV should not be made solely on demonstration of Gardnerella species on a HVS in the absence of symptoms. A HVS is not indicated in the absence of symptoms of vaginal discharge and is not part of a routine STI screen.
- Consider sexually transmitted causes of vaginal discharge on the basis of sexual history and consider testing for chlamydia and gonorrhoea.
- No benefit in treating male partners
- Women experiencing repeated episodes of Bacterial Vaginosis may benefit from using lactic acid vaginal gels to facilitate restoration of the normal vaginal flora. Preparations are available over the counter in pharmacies. Repeated episodes are more frequent in women who practice vaginal douching.
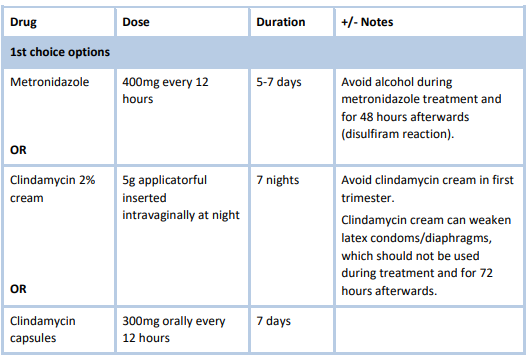
Treatment
Patient Information
Safe Prescribing
Visit the safe prescribing page
- Doses are oral and for adults unless otherwise stated
- Renal impairment dosing table
- Safety in Pregnancy and Lactation
- Drug interactions table. Extensive drug interactions for clarithromycin, fluoroquinolones, azole antifungals and rifampicin. Many antibiotics increase the risk of bleeding with anticoagulants.
- Visit the Health Products Regulatory Authority (HPRA) website for detailed drug information (summary of product characteristics and patient information leaflets). Dosing details, contraindications and drug interactions can also be found in the Irish Medicines Formulary (IMF) or other reference sources such as British National Formulary (BNF) / BNF for children (BNFC).
Reviewed June 2021